A major difference between both the forms of analysis is the time frame over which they are conducted.
An investor who wishes to invest in a business for a longer period of time (say more than 3 years), it becomes very important to understand the business in-depth from various perspectives, and hence fundamental analysis comes in play.
A trader who aims at intra-day profits needs to have understanding of trends in price and volume, and it is more important to understand – the entry, exit and risk perspective, and this is where technical analysis comes to play.
So, if the objective is intra-day gain, then one needs to capitalize on daily short term noise in the stock prices/markets through technical analysis, and it is long term gain, then one needs to concentrate on the underlying business performance through the fundamental analysis.
Fundamental analysis is a technique used for deriving stocks current fair value and forecast future value, mainly looking at economy, sector, company and political level. These include analysis of financial data, management, business concept, competition, and supply and demand forces.
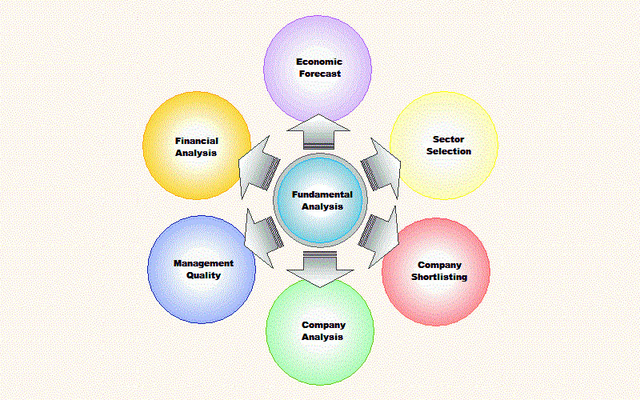
General Steps to Fundamental Evaluation:
- Economic forecast: Economic expansion and contraction can be linked to Interest rates, which is the leading economic indicator. When the economy expands, most of the sectors and companies benefits and grows, and when the economy declines, most of the sectors and companies usually suffer.
- Sector Selection: Basis current economic environment, and future economic forecast, potential strongest sectors needs to be shortlisted. To assess such potential, one have to look at the overall growth rate, market size, and other relevant factors.
- Company Short listing: This task includes finding the leaders and the innovators within a group. The first task is to identify the current business and competitive environment within a group as well as the future trends. A comparative analysis of the competition within a sector will help in identifying those companies with an edge and those most likely to succeed.
- Company analysis: Analyzing the resources and capabilities within each company would help in identifying those companies that are capable of creating and maintaining a competitive advantage. The analysis could focus on selecting companies with a sensible business plan, solid management and sound financials.
- Management Quality: Business plan execution is all dependent on the quality of management, depends on their past track record, and whether management is capable to deliver on its promises.
- Financial Analysis: There are different types of valuation metrics and much of it depends on the industry and stage of the economic cycle. A complete financial model can be built to forecast future revenues, expenses and profits. Companies then have to be ranked based on the valuation ratios such as Price/Book Value, Price/Earnings, etc. Those at the high end may be considered overvalued, while those at the low end may constitute relatively good value.
The final step of the fundamental analysis process is to combine all data, analysis and understanding into actual value picks.
The tools required for fundamental analysis are extremely basic, most of which are available for free:
- Company’s Annual report–This report can be downloaded from the company’s website for free.
- Industry related data – Basic data is available for free, and is usually published in the industry’s association website.
- Access to news –A good business news paper or services such as Google Alert can help you stay abreast of the latest news.
- MS Excel – Although not free, MS Excel can be extremely helpful in fundamental calculations.
To be Continued…




What’s up,I check your blog named “Technical Analysis VS Fundamental Analysis | Proficient Blog” daily.Your writing style is awesome, keep it up! And you can look our website about تنزيل اغانى.